Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Distributed Array#
This example shows how to use the pylops_mpi.DistributedArray.
This class provides a way to distribute arrays across multiple processes in
a parallel computing environment.
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from mpi4py import MPI
from pylops_mpi.DistributedArray import local_split, Partition
import pylops_mpi
plt.close("all")
np.random.seed(42)
# MPI parameters
size = MPI.COMM_WORLD.Get_size() # number of nodes
rank = MPI.COMM_WORLD.Get_rank() # rank of current node
# Defining the global shape of the distributed array
global_shape = (10, 5)
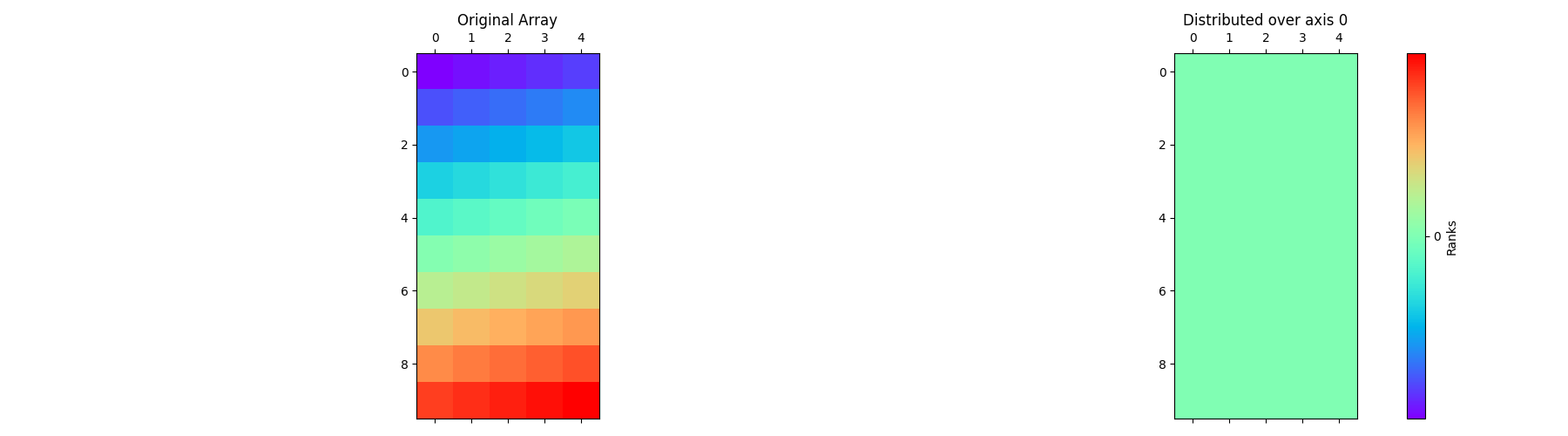
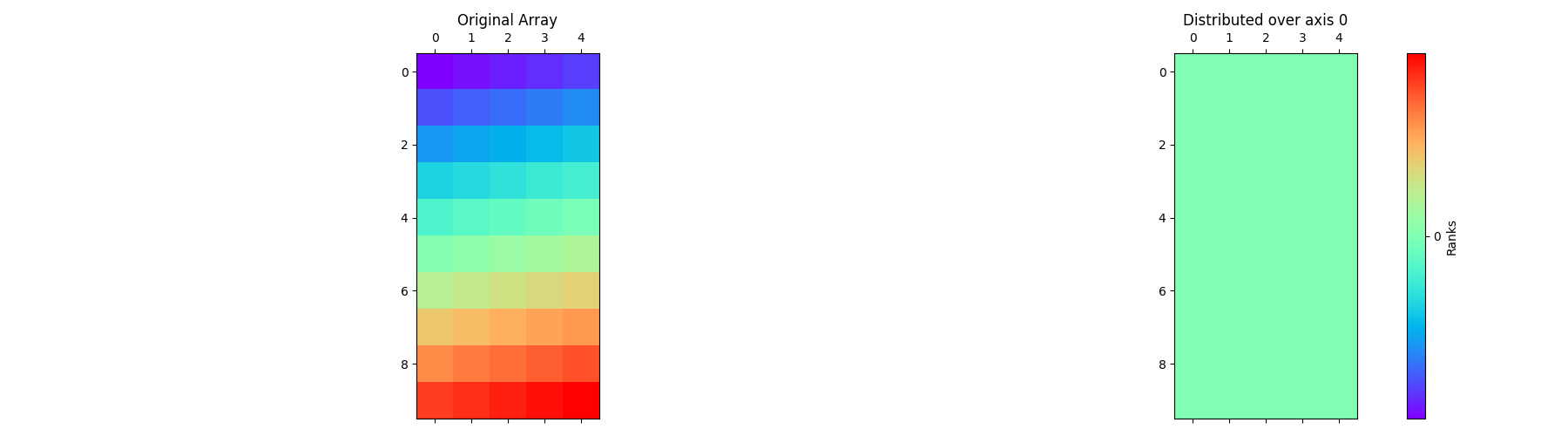
Let’s start by defining the class with the input parameters global_shape,
partition, and axis. Here’s an example implementation of the class
with axis=0.
arr = pylops_mpi.DistributedArray(global_shape=global_shape,
partition=pylops_mpi.Partition.SCATTER,
axis=0)
# Filling the local arrays
arr[:] = np.arange(arr.local_shape[0] * arr.local_shape[1] * arr.rank,
arr.local_shape[0] * arr.local_shape[1] * (arr.rank + 1)).reshape(arr.local_shape)
pylops_mpi.plot_distributed_array(arr)
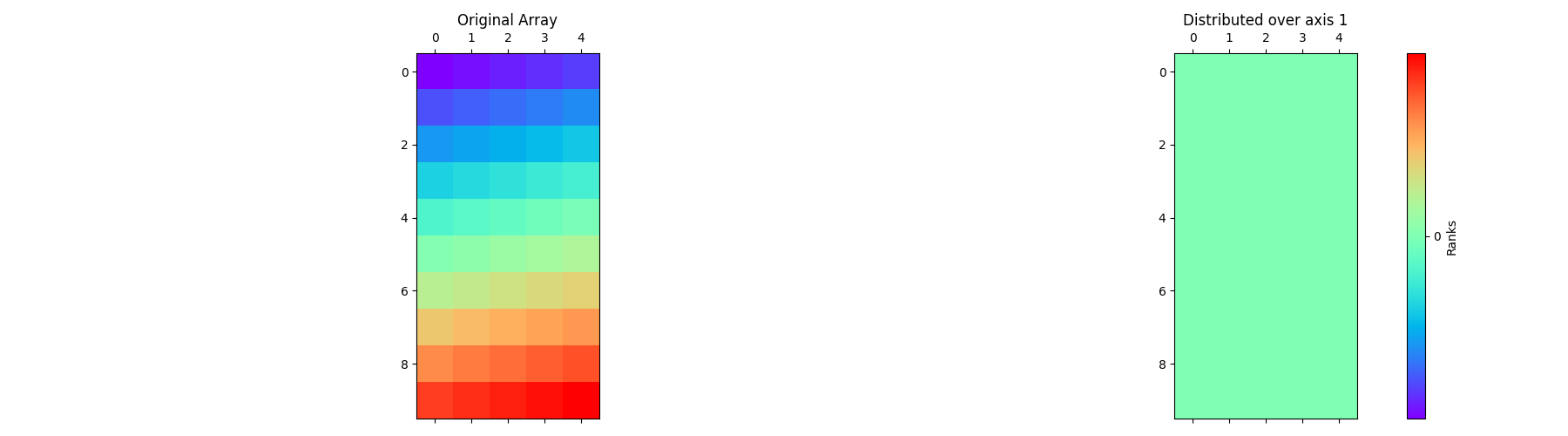
Below is an implementation to show how the global array is distributed along the second axis.
arr = pylops_mpi.DistributedArray(global_shape=global_shape,
partition=pylops_mpi.Partition.SCATTER,
axis=1)
# Filling the local arrays
arr[:] = np.arange(arr.local_shape[0] * arr.local_shape[1] * arr.rank,
arr.local_shape[0] * arr.local_shape[1] * (arr.rank + 1)).reshape(arr.local_shape)
pylops_mpi.plot_distributed_array(arr)
You also have the option of directly including the local_shapes as a parameter
to the pylops_mpi.DistributedArray. This will enable the assignment
of shapes to local arrays on each rank. However, it’s essential to ensure that
the number of processes matches the length of local_shapes, and that the
combined local shapes should align with the global_shape along the desired axis.
local_shape = local_split(global_shape, MPI.COMM_WORLD, Partition.SCATTER, 0)
# Assigning local_shapes(List of tuples)
local_shapes = MPI.COMM_WORLD.allgather(local_shape)
arr = pylops_mpi.DistributedArray(global_shape=global_shape, local_shapes=local_shapes, axis=0)
arr[:] = np.arange(arr.local_shape[0] * arr.local_shape[1] * arr.rank,
arr.local_shape[0] * arr.local_shape[1] * (arr.rank + 1)).reshape(arr.local_shape)
pylops_mpi.plot_distributed_array(arr)
To convert a random NumPy array into a pylops_mpi.DistributedArray,
you can use the to_dist classmethod. This method allows you to distribute
the array across multiple processes for parallel computation.
Below is an example implementation depicting the same.
n = global_shape[0] * global_shape[1]
# Array to be distributed
array = np.arange(n) / float(n)
arr1 = pylops_mpi.DistributedArray.to_dist(x=array.reshape(global_shape), axis=1)
array = array / 2.0
arr2 = pylops_mpi.DistributedArray.to_dist(x=array.reshape(global_shape), axis=1)
# plot local arrays
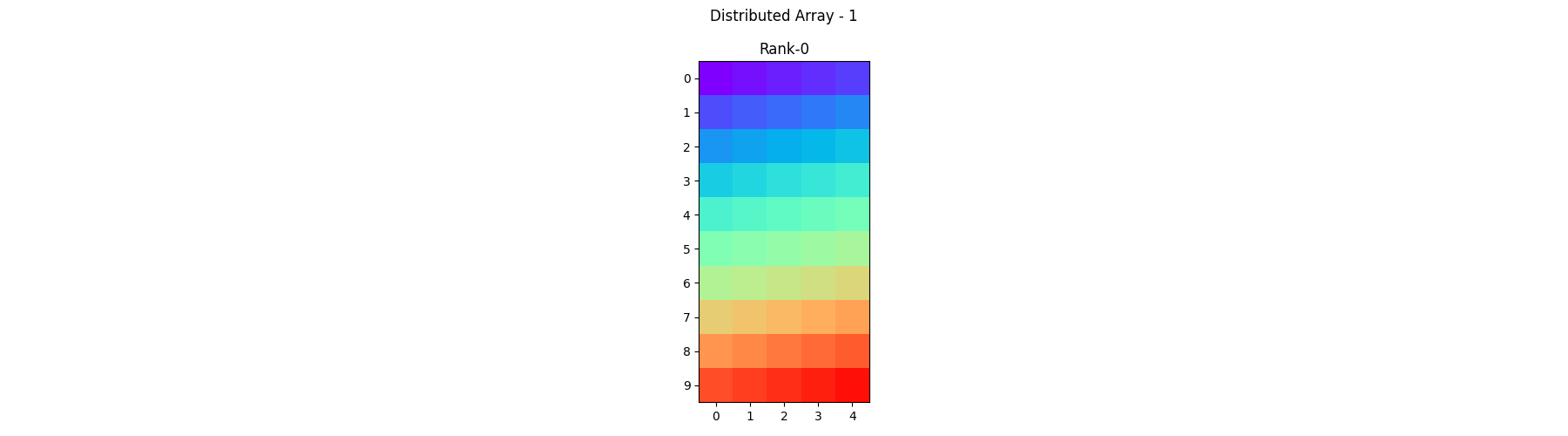
pylops_mpi.plot_local_arrays(arr1, "Distributed Array - 1", vmin=0, vmax=1)
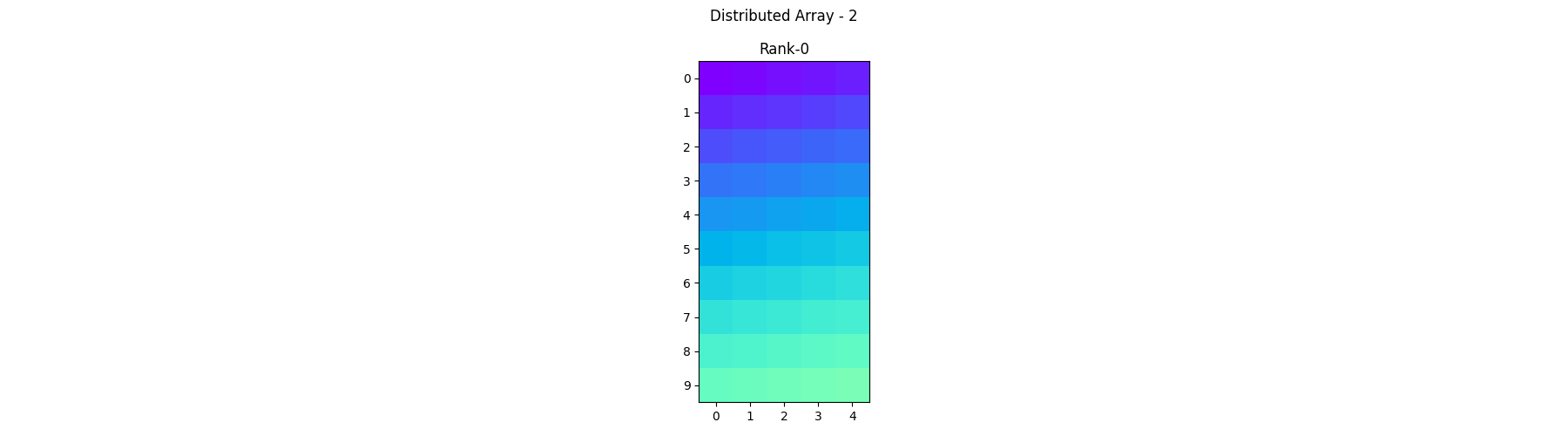
pylops_mpi.plot_local_arrays(arr2, "Distributed Array - 2", vmin=0, vmax=1)
Let’s move now to consider various operations that one can perform on
pylops_mpi.DistributedArray objects.
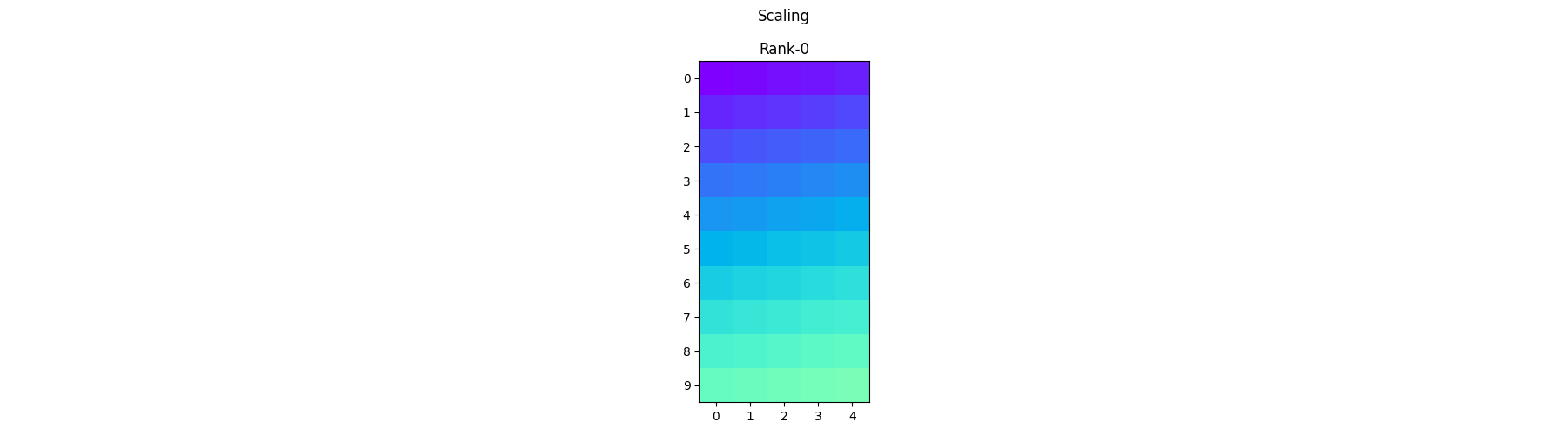
Scaling - Each process operates on its local portion of the array and scales the corresponding elements by a given scalar.
scale_arr = .5 * arr1
pylops_mpi.plot_local_arrays(scale_arr, "Scaling", vmin=0, vmax=1)
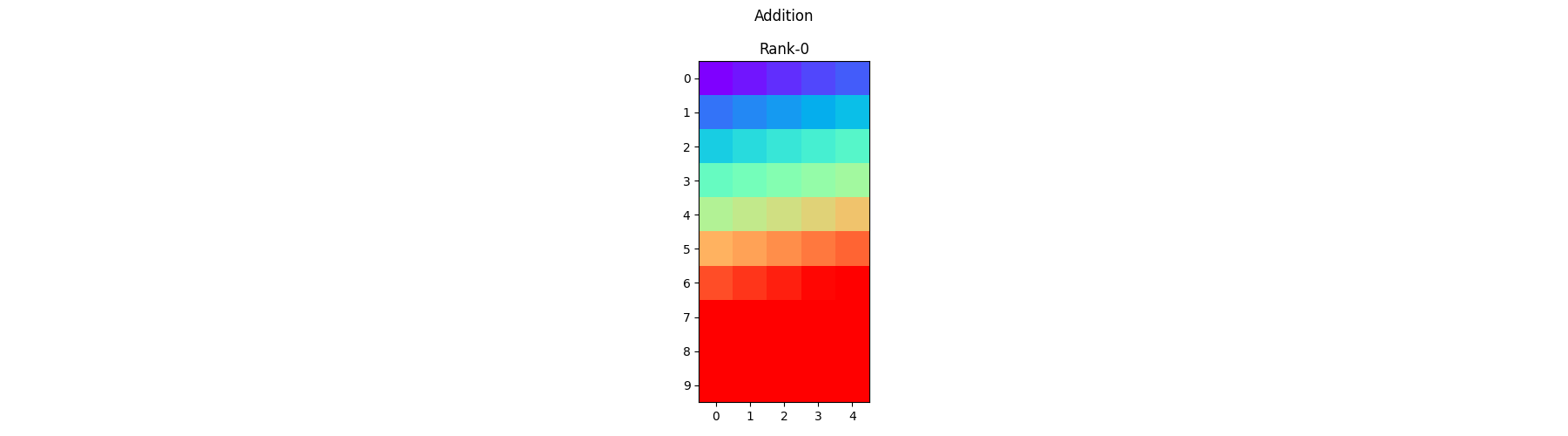
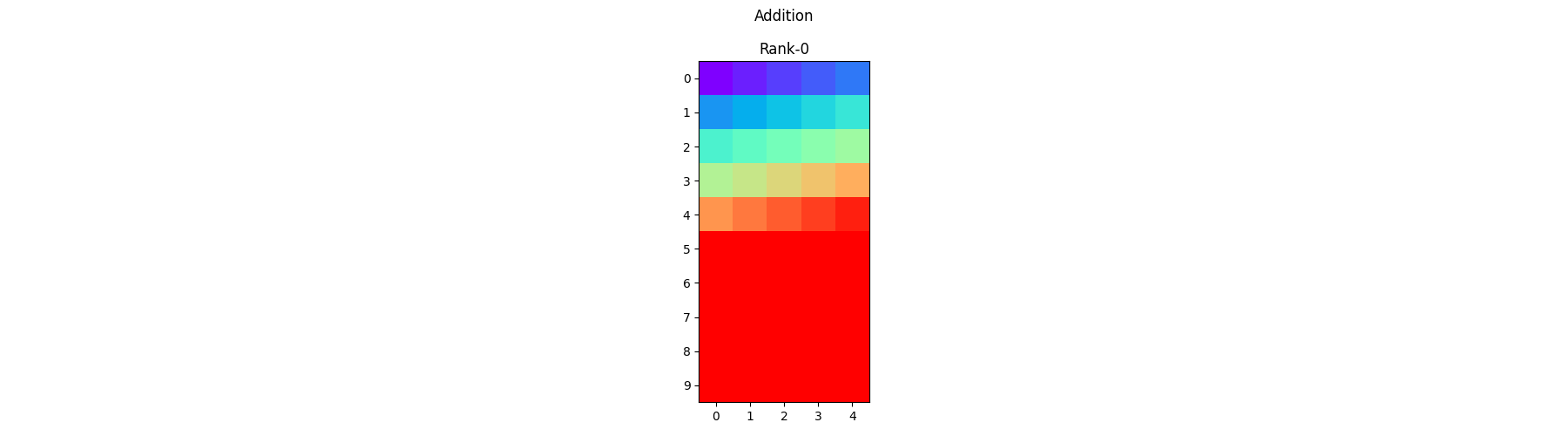
Element-wise Addition - Each process operates on its local portion of the array and adds the corresponding elements together.
sum_arr = arr1 + arr2
pylops_mpi.plot_local_arrays(sum_arr, "Addition", vmin=0, vmax=1)
Element-wise In-place Addition - Similar to the previous one but the addition is performed directly on one of the addends without creating a new distributed array.
sum_arr += arr2
pylops_mpi.plot_local_arrays(sum_arr, "Addition", vmin=0, vmax=1)
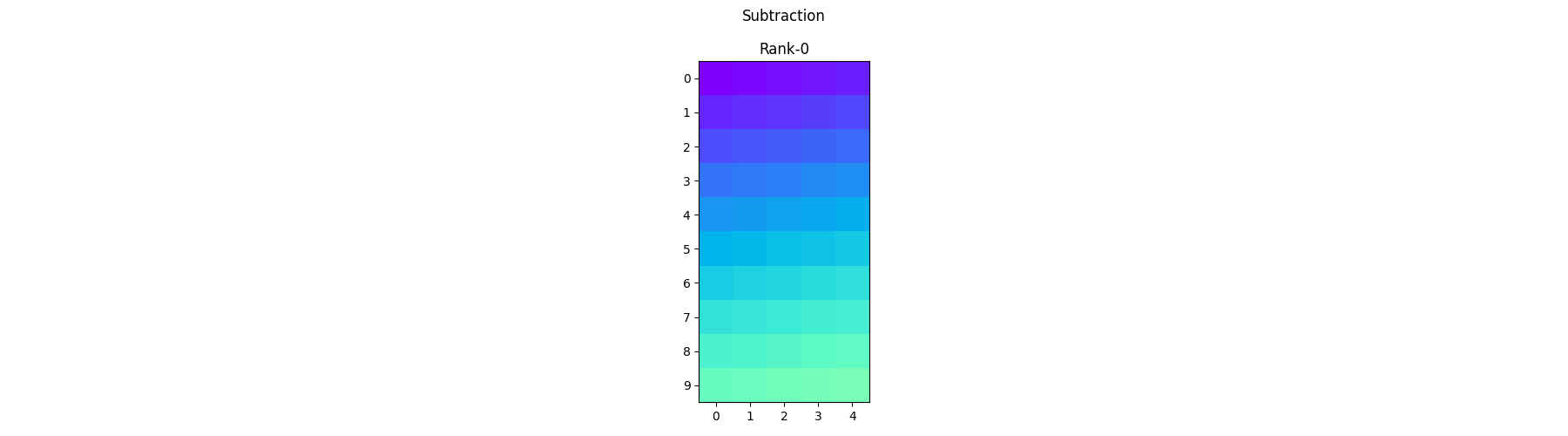
Element-wise Subtraction - Each process operates on its local portion of the array and subtracts the corresponding elements together.
diff_arr = arr1 - arr2
pylops_mpi.plot_local_arrays(diff_arr, "Subtraction", vmin=0, vmax=1)
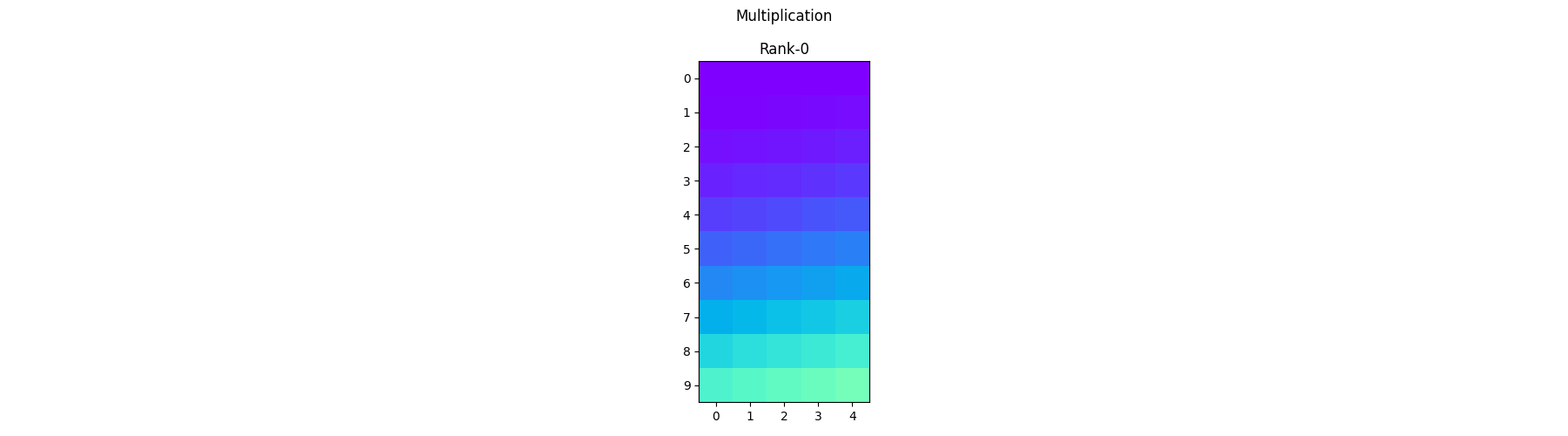
Element-wise Multiplication - Each process operates on its local portion of the array and multiplies the corresponding elements together.
mult_arr = arr1 * arr2
pylops_mpi.plot_local_arrays(mult_arr, "Multiplication", vmin=0, vmax=1)
Finally, let’s look at the case where parallelism could be applied over
multiple axes - and more specifically one belonging to the model/data and one
to the operator. This kind of “2D”-parallelism requires repeating parts of
the model/data over groups of ranks. However, when global operations such as
dot or norm are applied on a pylops_mpi.DistributedArray of
this kind, we need to ensure that the repeated portions to do all contribute
to the computation. This can be achieved via the mask input parameter:
a list of size equal to the number of ranks, whose elements contain the index
of the subgroup/subcommunicator (with partial arrays in different groups
are identical to each other).
# Defining the local and global shape of the distributed array
local_shape = 5
global_shape = local_shape * size
# Create mask
nsub = 2
subsize = max(1, size // nsub)
mask = np.repeat(np.arange(size // subsize), subsize)
if rank == 0:
print("1D masked arrays")
print(f"Mask: {mask}")
# Create and fill the distributed array
x = pylops_mpi.DistributedArray(global_shape=global_shape,
partition=Partition.SCATTER,
mask=mask)
x[:] = (MPI.COMM_WORLD.Get_rank() % subsize + 1.) * np.ones(local_shape)
xloc = x.asarray()
xloc1 = x.asarray(masked=True)
if rank == 0:
print('xloc (with repeated portions)', xloc)
print('xloc (only effective portions):', xloc1)
# Dot product
dot = x.dot(x)
dotloc = np.dot(xloc[local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize):local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize + 1)],
xloc[local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize):local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize + 1)])
print(f"Dot check (Rank {rank}): {np.allclose(dot, dotloc)}")
# Norm
norm = x.norm(ord=2)
normloc = np.linalg.norm(xloc[local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize):local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize + 1)],
ord=2)
print(f"Norm check (Rank {rank}): {np.allclose(norm, normloc)}")
1D masked arrays
Mask: [0]
xloc (with repeated portions) [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
xloc (only effective portions): [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
Dot check (Rank 0): True
Norm check (Rank 0): True
And with 2d-arrays distributed over axis=1
extra_dim_shape = 2
if rank == 0:
print("2D masked arrays (over axis=1)")
# Create and fill the distributed array
x = pylops_mpi.DistributedArray(global_shape=(extra_dim_shape, global_shape),
partition=Partition.SCATTER,
axis=1, mask=mask)
x[:] = (MPI.COMM_WORLD.Get_rank() % subsize + 1.) * np.ones((extra_dim_shape, local_shape))
xloc = x.asarray()
# Dot product
dot = x.dot(x)
dotloc = np.dot(xloc[:, local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize):local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize + 1)].ravel(),
xloc[:, local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize):local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize + 1)].ravel())
print(f"Dot check (Rank {rank}): {np.allclose(dot, dotloc)}")
# Norm
norm = x.norm(ord=2, axis=1)
normloc = np.linalg.norm(xloc[:, local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize):local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize + 1)],
ord=2, axis=1)
print(f"Norm check (Rank {rank}): {np.allclose(norm, normloc)}")
2D masked arrays (over axis=1)
Dot check (Rank 0): True
Norm check (Rank 0): True
And finally with 2d-arrays distributed over axis=0
if rank == 0:
print("2D masked arrays (over axis=0)")
# Create and fill the distributed array
x = pylops_mpi.DistributedArray(global_shape=(global_shape, extra_dim_shape),
partition=Partition.SCATTER,
axis=0, mask=mask)
x[:] = (MPI.COMM_WORLD.Get_rank() % subsize + 1.) * np.ones((local_shape, extra_dim_shape))
xloc = x.asarray()
# Dot product
dot = x.dot(x)
dotloc = np.dot(xloc[local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize):local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize + 1)].ravel(),
xloc[local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize):local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize + 1)].ravel())
print(f"Dot check (Rank {rank}): {np.allclose(dot, dotloc)}")
# Norm
norm = x.norm(ord=2, axis=0)
normloc = np.linalg.norm(xloc[local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize):local_shape * subsize * (rank // subsize + 1)],
ord=2, axis=0)
print(f"Norm check (Rank {rank}): {np.allclose(norm, normloc)}")
2D masked arrays (over axis=0)
Dot check (Rank 0): True
Norm check (Rank 0): True
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.180 seconds)