Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Multi-Dimensional Convolution#
This example shows how to use the pylops_mpi.waveeqprocessing.MPIMDC operator
to convolve a 3D kernel with an input seismic data in a distributed fashion (where
parallelism is harnessed over the frequency axis when performing repeated matrix-vector
or matrix-matrix multiplications).
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from mpi4py import MPI
from pylops.utils.seismicevents import hyperbolic2d, makeaxis
from pylops.utils.tapers import taper3d
from pylops.utils.wavelets import ricker
from pylops_mpi.DistributedArray import local_split, Partition
import pylops_mpi
plt.close("all")
np.random.seed(42)
rank = MPI.COMM_WORLD.Get_rank()
size = MPI.COMM_WORLD.Get_size()
dtype = np.float32
cdtype = np.complex64
Let’s start by creating a set of hyperbolic events to be used as our MDC kernel
# Input parameters
par = {
"ox": -300,
"dx": 10,
"nx": 61,
"oy": -500,
"dy": 10,
"ny": 101,
"ot": 0,
"dt": 0.004,
"nt": 400,
"f0": 20,
"nfmax": 200,
}
t0_m = 0.2
vrms_m = 1100.0
amp_m = 1.0
t0_G = (0.2, 0.5, 0.7)
vrms_G = (1200.0, 1500.0, 2000.0)
amp_G = (1.0, 0.6, 0.5)
# Taper
tap = taper3d(par["nt"], (par["ny"], par["nx"]), (5, 5), tapertype="hanning")
# Create axis
t, t2, x, y = makeaxis(par)
# Create wavelet
wav = ricker(t[:41], f0=par["f0"])[0]
# Generate model
m, mwav = hyperbolic2d(x, t, t0_m, vrms_m, amp_m, wav)
# Generate operator
G, Gwav = np.zeros((par["ny"], par["nx"], par["nt"])), np.zeros(
(par["ny"], par["nx"], par["nt"])
)
for iy, y0 in enumerate(y):
G[iy], Gwav[iy] = hyperbolic2d(x - y0, t, t0_G, vrms_G, amp_G, wav)
G, Gwav = G * tap, Gwav * tap
# Add negative part to data and model
m = np.concatenate((np.zeros((par["nx"], par["nt"] - 1)), m), axis=-1)
mwav = np.concatenate((np.zeros((par["nx"], par["nt"] - 1)), mwav), axis=-1)
Gwav2 = np.concatenate((np.zeros((par["ny"], par["nx"], par["nt"] - 1)), Gwav), axis=-1)
# Move to frequency
Gwav_fft = np.fft.rfft(Gwav2, 2 * par["nt"] - 1, axis=-1)
Gwav_fft = Gwav_fft[..., : par["nfmax"]]
# Move frequency/time to first axis
m, mwav = m.T, mwav.T
Gwav_fft = Gwav_fft.transpose(2, 0, 1)
Now that we have created the kernel of our MDC operator in Gwav_fft, we
are ready to define a strategy on how to split it along the first
(i.e., frequency) axis over different ranks. In practical applications, one
would of course pre-compute the kernel and just load the relevant part in
each rank from file.
# Choose how to split sources to ranks
nf = par["nfmax"]
nf_rank = local_split((nf, ), MPI.COMM_WORLD, Partition.SCATTER, 0)
nf_ranks = np.concatenate(MPI.COMM_WORLD.allgather(nf_rank))
ifin_rank = np.insert(np.cumsum(nf_ranks)[:-1] , 0, 0)[rank]
ifend_rank = np.cumsum(nf_ranks)[rank]
print(f'Rank: {rank}, nf: {nf_rank}, ifin: {ifin_rank}, ifend: {ifend_rank}')
# Extract part of kernel of interest
G = Gwav_fft[ifin_rank:ifend_rank].astype(cdtype)
print(f'Rank: {rank}, G: {G.shape}')
Rank: 0, nf: (200,), ifin: 0, ifend: 200
Rank: 0, G: (200, 101, 61)
We can finally create the MDC operator using
pylops_mpi.waveeqprocessing.MPIMDC so that the most
demanding computations can be run in parallel.
# Define operator
Fop = pylops_mpi.waveeqprocessing.MPIMDC(
G, nt=2 * par["nt"] - 1, nv=1, nfreq=nf,
dt=0.004, dr=1.0, twosided=True)
# Apply forward
md = pylops_mpi.DistributedArray(global_shape=(2 * par["nt"] - 1) * par["nx"] * 1,
partition=pylops_mpi.Partition.BROADCAST,
dtype=dtype)
md[:] = m.astype(dtype).ravel()
dd = Fop @ md
d = dd.asarray().real
d = d.reshape(2 * par["nt"] - 1, par["ny"])
# Apply adjoint
madjd = Fop.H @ dd
madj = madjd.asarray().real
madj = madj.reshape(2 * par["nt"] - 1, par["nx"])
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.11.14/x64/lib/python3.11/site-packages/pylops/signalprocessing/fft.py:59: UserWarning: numpy backend always returns complex128 dtype. To respect the passed dtype, data will be casted to complex64.
warnings.warn(
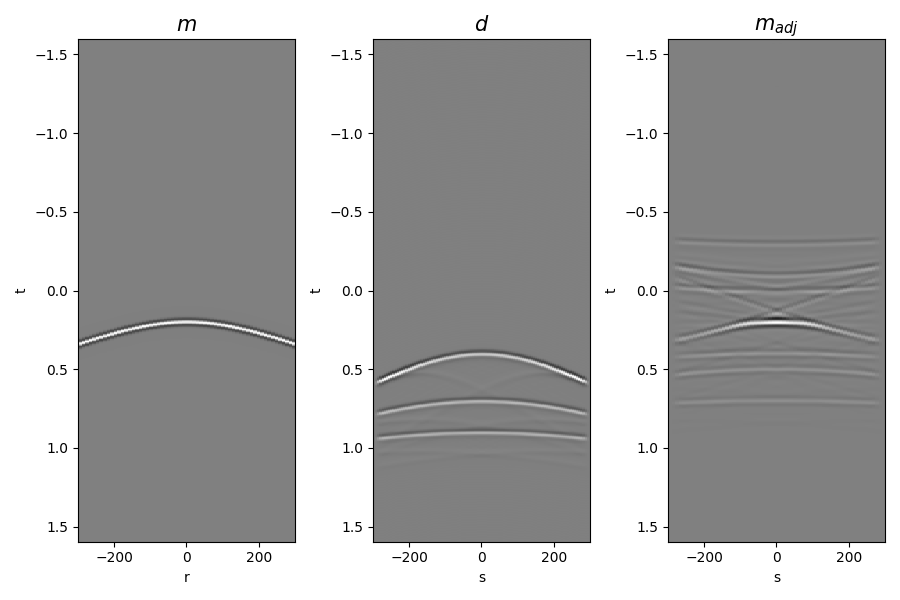
Finally let’s display input model, data and adjoint model
if rank == 0:
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(9, 6))
axs[0].imshow(
mwav,
aspect="auto",
interpolation="nearest",
cmap="gray",
vmin=-mwav.max(),
vmax=mwav.max(),
extent=(x.min(), x.max(), t2.max(), t2.min()),
)
axs[0].set_title(r"$m$", fontsize=15)
axs[0].set_xlabel("r")
axs[0].set_ylabel("t")
axs[1].imshow(
d,
aspect="auto",
interpolation="nearest",
cmap="gray",
vmin=-d.max(),
vmax=d.max(),
extent=(x.min(), x.max(), t2.max(), t2.min()),
)
axs[1].set_title(r"$d$", fontsize=15)
axs[1].set_xlabel("s")
axs[1].set_ylabel("t")
axs[2].imshow(
madj,
aspect="auto",
interpolation="nearest",
cmap="gray",
vmin=-madj.max(),
vmax=madj.max(),
extent=(x.min(), x.max(), t2.max(), t2.min()),
)
axs[2].set_title(r"$m_{adj}$", fontsize=15)
axs[2].set_xlabel("s")
axs[2].set_ylabel("t")
fig.tight_layout()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.453 seconds)